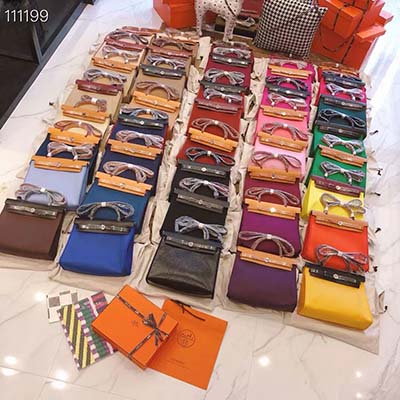
ubuntu clone boot partition | ubuntu bootable clone image ubuntu clone boot partition Clone current Linux partition to target partition. Generate and update UUID for target partition. Update grub and fstab. Update MBR to point the new grub. Few assumptions I . Jakarta - Seorang sosialita asal Indonesia baru-baru ini bikin heboh. Dia ditangkap atas dugaan pencurian tas mewah di Australia. Warga negara Indonesia yang tak disebutkan namanya itu mencuri 2 tas Louis Vuitton di toko kawasan Jalan Whiteman, Melbourne, Australia. Jika ditotal, harga tas yang dicuri mencapai AUD 11 ribu atau .
0 · ubuntu clone entire disk
1 · ubuntu clone bootable disk
2 · ubuntu bootable clone image
3 · ubuntu boot clone windows 10
4 · ubuntu boot clone
5 · how to copy ubuntu partition
6 · clone bootable boot disk
7 · bootable clone for ubuntu
Futbola Skolu Metta par savu izvēlas tie, kas vēlas visaugstākā līmeņa personības attīstību un īpaši profesionālu futbola apmācību. Latvijas futbola federācija sešus gadus atzinusi Mettu par radošāko bērnu un jauniešu futbola klubu Latvijā, bet Rīgas Dome par labāko sporta organizāciju.
Choose disk to disk and clone away! Then, for your sanity's sake, once the disk-to-disk cloning completes, image the system with Clonezilla, saving the partitions (which will be . Boot from a live system, plug in the new HDD via USB (or another (s)ata cable, depending on your hardware), and start a 'Terminal'. Check what is the path for your old HDD . Clone current Linux partition to target partition. Generate and update UUID for target partition. Update grub and fstab. Update MBR to point the new grub. Few assumptions I . I'm trying to move my Ubuntu installation to a new SSD but all the guides that I found are either incomplete or the partition layout is different than mine. I would use Ubuntu live and clone the sdd5 partition with gparted to the .
What I want to do is export my Ubuntu OS in its current state (installed programs, config files, media, etc) to the USB stick so that all of the data is stored on the stick, and I can .
In this tutorial, we saw how to clone a disk’s partition on Linux. The stock dd tool suffices for the job, but extra applications are also available like Partimage, Clonezilla, and a slew of others that we did not cover here.
Just open ubuntu and install gparted, umount all partitions that you want to clone. Select partition from usb A in Gparted and copy >> paste to another usb B. sdb2 (Ubuntu backup) is the intended clone of the Ubuntu system and user files, shortly, the root partition. As sdb is an external device, sdb2 is mounted by default as /media/alba/Ubuntu backup . sdb1 is the intended clone of the EFI system partition, mounted as /media/alba/EFI .
Choose disk to disk and clone away! Then, for your sanity's sake, once the disk-to-disk cloning completes, image the system with Clonezilla, saving the partitions (which will be compressed) to the target drive's root or /home partition. . Boot from a live system, plug in the new HDD via USB (or another (s)ata cable, depending on your hardware), and start a 'Terminal'. Check what is the path for your old HDD (probably /dev/sda), and the new one as well (/dev/sdb), and issue this command: sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb status=progress. Cloning your hard drive to an image file with dd is incredibly simple. First, you will need to figure out the name of the drive you want to clone. There are a few ways to do this, but here we are just using lsblk to list your drives and all their partitions.
If you only want to clone a partition of your Linux disk drive, use: dd if=/dev/sda1 of=/dev/sdb1 bs=64K conv=noerror,sync. As you can see, dd will clone partition sda1 (partition 1 on device sda) to sdb1, a newly created partition 1 on device sdb. Clone current Linux partition to target partition. Generate and update UUID for target partition. Update grub and fstab. Update MBR to point the new grub. Few assumptions I make are: Your Ubuntu is 9.10 or later. Your Ubuntu is on ext4 partition (gparted should be to copy/paste any other file-system as well, however these steps were tested on ext4) I'm trying to move my Ubuntu installation to a new SSD but all the guides that I found are either incomplete or the partition layout is different than mine. I would use Ubuntu live and clone the sdd5 partition with gparted to the new ssd. What I want to do is export my Ubuntu OS in its current state (installed programs, config files, media, etc) to the USB stick so that all of the data is stored on the stick, and I can boot into it from another machine.
In this tutorial, we saw how to clone a disk’s partition on Linux. The stock dd tool suffices for the job, but extra applications are also available like Partimage, Clonezilla, and a slew of others that we did not cover here. Just open ubuntu and install gparted, umount all partitions that you want to clone. Select partition from usb A in Gparted and copy >> paste to another usb B.
sdb2 (Ubuntu backup) is the intended clone of the Ubuntu system and user files, shortly, the root partition. As sdb is an external device, sdb2 is mounted by default as /media/alba/Ubuntu backup . sdb1 is the intended clone of the EFI system partition, mounted as /media/alba/EFI .
Choose disk to disk and clone away! Then, for your sanity's sake, once the disk-to-disk cloning completes, image the system with Clonezilla, saving the partitions (which will be compressed) to the target drive's root or /home partition. .
Boot from a live system, plug in the new HDD via USB (or another (s)ata cable, depending on your hardware), and start a 'Terminal'. Check what is the path for your old HDD (probably /dev/sda), and the new one as well (/dev/sdb), and issue this command: sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/sdb status=progress. Cloning your hard drive to an image file with dd is incredibly simple. First, you will need to figure out the name of the drive you want to clone. There are a few ways to do this, but here we are just using lsblk to list your drives and all their partitions.
omega seamaster aqua terra 150 m co-axial day-date
If you only want to clone a partition of your Linux disk drive, use: dd if=/dev/sda1 of=/dev/sdb1 bs=64K conv=noerror,sync. As you can see, dd will clone partition sda1 (partition 1 on device sda) to sdb1, a newly created partition 1 on device sdb. Clone current Linux partition to target partition. Generate and update UUID for target partition. Update grub and fstab. Update MBR to point the new grub. Few assumptions I make are: Your Ubuntu is 9.10 or later. Your Ubuntu is on ext4 partition (gparted should be to copy/paste any other file-system as well, however these steps were tested on ext4)
I'm trying to move my Ubuntu installation to a new SSD but all the guides that I found are either incomplete or the partition layout is different than mine. I would use Ubuntu live and clone the sdd5 partition with gparted to the new ssd. What I want to do is export my Ubuntu OS in its current state (installed programs, config files, media, etc) to the USB stick so that all of the data is stored on the stick, and I can boot into it from another machine. In this tutorial, we saw how to clone a disk’s partition on Linux. The stock dd tool suffices for the job, but extra applications are also available like Partimage, Clonezilla, and a slew of others that we did not cover here.
ubuntu clone entire disk
omega seamaster aqua terra 150m james bond spectre limited edition

omega seamaster aqua terra amazon
omega seamaster aqua terra 150m quartz 38.5 mm
omega seamaster aqua terra 2017 illumination
To be the leading football club in Latvia with highly-rated sports program and elite football academy. The football club that is acknowledged in Europe for being able to develop Latvia born or raised world-class footballers and educated professionals for .
ubuntu clone boot partition|ubuntu bootable clone image