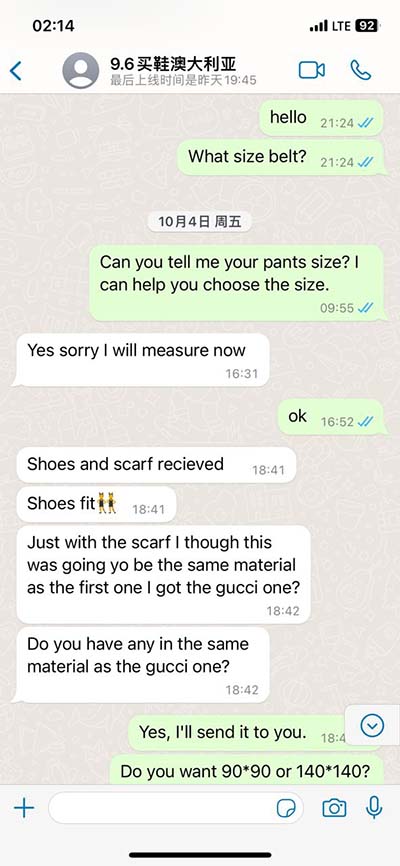
lv pv | wwwvivi latvija lv pv To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. . The biggest CROCS footwear selection for women, men and kids in the country. High quality, long lifetime CROCS shoes. Free delivery in 1-2 working days!
0 · wwwvivi latvija
1 · www.pv.lv
2 · vilcienu karte
3 · vilciens rīga viļņa
4 · vilciens rīga dubulti
5 · pv vilciens
6 · latvijas vilcienu karte
7 · latvijas vilciens
YOUNGSTOWN, Ohio (WKBN) — An Austintown man accused of beating a Beaver Township police officer and prompting an hours-long manhunt received his sentence in Mahoning County Court of Common Pleas on.
wwwvivi latvija
This review focuses on the fundamentals of left ventricular (LV) PV analysis highlighting practical aspects of PV measurements, interpretation of signals and potential applications to clinical .
www.pv.lv
To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. .This review focuses on the fundamentals of left ventricular (LV) PV analysis highlighting practical aspects of PV measurements, interpretation of signals and potential applications to clinical practice.
To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. When this is done, a PV loop is generated (bottom panel of figure and linked YouTube video). A PV loop plots the changes in ventricular pressure associated with the changes in volume which occur during the cardiac cycle. The plot of a ventricular pressure-volume loop contains the following information: Volumes: End-diastolic volume (where the mitral valve closes) End-systolic volume (where the aortic valve closes) Pressure-volume (PV) analysis addresses these shortcomings by combining simultaneous measurements of pressure and volume to generate load-independent measures of systolic and diastolic chamber properties, and is considered the gold-standard method for characterizing ventricular systolic and diastolic function, as well as ventricular-vascular int.
Real-time left ventricular (LV) pressure–volume loops provide a framework for understanding cardiac mechanics in experimental animals and humans. Such loops can be generated by real-time measurement of pressure and volume within the left ventricle.
Simultaneous in vivo pressure-volume (PV) measurements with a conductance catheter (CC) placed in the LV allow real-time assessment of the LV PV relationship. 10 In fact, percutaneous MVR provides a unique pathophysiological model for assessing the immediate hemodynamic effects of MR reduction on LV performance, eliminating any confounding . Left Ventricular P-V Loop: Plot of left ventricular volume versus pressure. Time is not directly demonstrated on this graph, but the stages of the cardiac cycle can be inferred: A-B is isovolumetric relaxation. Ventricular pressure is less than aortic pressure but greater than atrial pressure, so both mitral and aortic valves are closed.
vilcienu karte
vilciens rīga viļņa
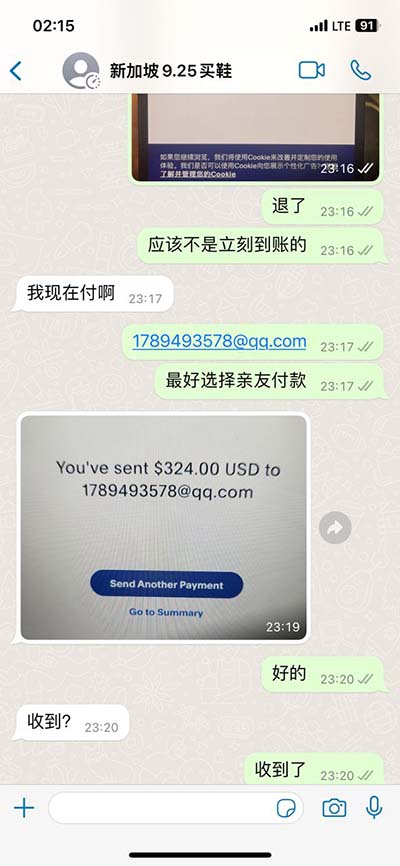
gucci shopping bijoux
In this study, we present the first experience with a fully noninvasive LV PV loop analysis across healthy controls, subjects with SDD, and patients with heart failure with preserved or impaired systolic function.
Ventricular pressure–volume (PV) analysis is the reference method for the study of cardiac mechanics. Advances in calibration algorithms and measuring techniques brought new perspectives for.
Introduction: The left ventricle (LV) pressure-volume loop (PV-loop) is a powerful tool for evaluating LV function. Current non-invasive cardiac MRI-based methods for estimating LV PV-loops provide limited diastolic LVP information (Circ .This review focuses on the fundamentals of left ventricular (LV) PV analysis highlighting practical aspects of PV measurements, interpretation of signals and potential applications to clinical practice.
To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. When this is done, a PV loop is generated (bottom panel of figure and linked YouTube video). A PV loop plots the changes in ventricular pressure associated with the changes in volume which occur during the cardiac cycle. The plot of a ventricular pressure-volume loop contains the following information: Volumes: End-diastolic volume (where the mitral valve closes) End-systolic volume (where the aortic valve closes)
Pressure-volume (PV) analysis addresses these shortcomings by combining simultaneous measurements of pressure and volume to generate load-independent measures of systolic and diastolic chamber properties, and is considered the gold-standard method for characterizing ventricular systolic and diastolic function, as well as ventricular-vascular int.Real-time left ventricular (LV) pressure–volume loops provide a framework for understanding cardiac mechanics in experimental animals and humans. Such loops can be generated by real-time measurement of pressure and volume within the left ventricle. Simultaneous in vivo pressure-volume (PV) measurements with a conductance catheter (CC) placed in the LV allow real-time assessment of the LV PV relationship. 10 In fact, percutaneous MVR provides a unique pathophysiological model for assessing the immediate hemodynamic effects of MR reduction on LV performance, eliminating any confounding .
Left Ventricular P-V Loop: Plot of left ventricular volume versus pressure. Time is not directly demonstrated on this graph, but the stages of the cardiac cycle can be inferred: A-B is isovolumetric relaxation. Ventricular pressure is less than aortic pressure but greater than atrial pressure, so both mitral and aortic valves are closed. In this study, we present the first experience with a fully noninvasive LV PV loop analysis across healthy controls, subjects with SDD, and patients with heart failure with preserved or impaired systolic function. Ventricular pressure–volume (PV) analysis is the reference method for the study of cardiac mechanics. Advances in calibration algorithms and measuring techniques brought new perspectives for.

vilciens rīga dubulti
pv vilciens
BANNING. $29,999. hide. 1 - 60 of 60. las vegas atvs, utvs, snowmobiles "polaris rzr 1000" - craigslist.
lv pv|wwwvivi latvija